A skin disease is a condition that affects the skin’s function, appearance, or texture. Examples include acne, psoriasis, eczema, rosacea, warts, skin cancer, and other skin illnesses. Some skin illnesses are inherited, while allergies, infections, or exposure to particular chemicals or environmental conditions bring others on.

Types of skin diseases
Some skin conditions are mild. Others result in severe symptoms. The following are among the most common skin diseases:
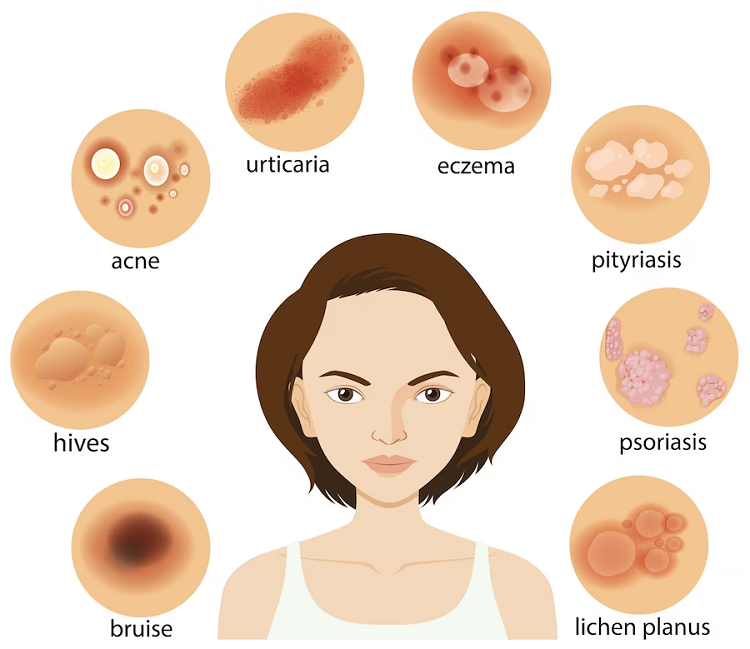
Acne, clogged skin follicles that cause oil, bacteria, & dead skin to accumulate in your pores.
- Acne is most typically found on the face, head, shoulders, torso, and upper back. Blackheads, Redness, whiteheads, pimples, deep, painful cysts & nodules are all symptoms of skin breakouts.
- Blisters are distinguished by a watery, transparent, fluid-filled skin patch. They can be smaller than one centimeter (cm) (vesicle) or greater than one centimeter (bulla), and they can exist alone or in groups. Blisters can appear on any part of the body.
- Alopecia areata is characterized by hair loss in tiny regions.
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis), dry, itchy skin that causes swelling, cracking, or scaliness.
- Psoriasis is characterized by scaly skin that may swell or feel hot.
- Raynaud’s phenomenon is characterized by a periodic decrease in blood flow to your fingers, toes, or other body parts, resulting in numbness, or skin color changes.
- Rosacea is characterized by flushing, thick skin, and pimples, which generally appear on the face.
- The uncontrolled development of abnormal skin cells causes skin cancer.
- Vitiligo is a condition in which patches of skin lose pigment.
Causes of skin disease
Infections
Infections are produced by the infiltration and proliferation of microorganisms within the body, such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Fungi, which can develop on the skin, nails, hair, and mucous surfaces, induce fungal diseases. Athlete’s foot, fungus, and candidiasis are examples of common fungal diseases.
Bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, which can infiltrate and proliferate in the body, producing symptoms such as temperature, chills, and discomfort. Strep throat, urinary tract infections, and asthma are all examples of common bacterial illnesses.
Viruses cause viral infections because they can infiltrate the body and attack cells, producing symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and muscular pains. Common viral illnesses include the flu, colds, and influenza.
Allergies
Allergies are an immune system overreaction to generally innocuous items such as pollen, food, dust, or pet dander. When the immune system encounters an allergen, it produces histamine and other substances that cause symptoms such as a runny nose, sneezing, itching, and hives. Some people may also have more severe responses, such as trouble breathing, edema, and anaphylaxis.
Inherited or genetic
Many variables are inherited or genetic, which means they are handed down from parents to their children via their genes. Here are a couple of examples:
The genes that a person gets from their parents decide their eye color. The genes that regulate eye color have the ability to affect the quantity and type of pigments in the iris, which gives the eye its color.
Blood type is decided by genes inherited from one’s ancestors. The presence or lack of certain antigens on the surface of red blood cells determines the existence or absence of blood kinds A, B, AB, and O.
Many genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, Huntington’s disease, and muscular dystrophy, can be passed from parents. These diseases are triggered by mutations in one or more chromosomes and can result in a variety of health issues.
Height is affected by a mix of hereditary and environmental variables. Genetic factors, however, are believed to play a bigger part in determining a person’s height. Several genes linked with height have been discovered through research, including those involved in bone growth and development.
- Certain diseases: Some diseases have a genetic component, indicating that a person’s chance of getting the disease is affected by their genes. Breast cancer, Alzheimer’s illness, and certain kinds of diabetes are examples.
- Environmental exposure: Environmental factors such as sunlight, toxins, and pollution can all have a negative effect on a person’s health and well-being. Here are some instances of how each can have an impact on health:
- Sunlight: Exposure to sunlight can be advantageous to the body because it contains vitamin D, which helps keep healthy bones and immune function. However, excessive solar contact can cause sunburn, accelerated ageing of the skin, and an increased chance of skin cancer.
- Chemicals: Chemical exposure in the atmosphere can occur through air pollution, contaminated drinking supplies, or chemical exposure in the workplace. Asbestos, lead, and benzene exposure can raise the chance of getting cancer, respiratory issues, and neurological diseases.
- Pollution: Environmental pollution, such as air pollution, can cause breathing issues such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer. Pollution can also have an impact on the arterial system, raising the chance of heart disease, stroke, and other circulatory issues.
Autoimmune conditions
Autoimmune diseases are caused by the immune system erroneously attacking and damaging the body’s own tissues and cells, mistaking them for external invaders. There are numerous kinds of autoimmune diseases, including: Arthritis rheumatoid, Lupus, Multiple sclerosis (MS), Diabetes mellitus type 1, Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Unbalanced hormones
This is are a disorder in which the levels of hormones in the body are not in the appropriate ratio, resulting in a variety of symptoms and health issues. Hormonal imbalances can arise from several causes, including age, stress, lifestyle changes, underlying medical disorders, and certain drugs. Thyroid diseases, menopause, adrenal insufficiency, and diabetes are all instances of hormonal abnormalities. Medication, lifestyle modifications, and hormone replacement treatment are often used to treat hormonal abnormalities.
Deficiencies in Nutritional
Nutrition deficiencies arise when the body is deficient in key vitamins, minerals, or other substances required for good health. These deficiencies can be caused by several circumstances, including an insufficient or imbalanced diet, poor nutrient absorption in the stomach, and medical diseases that interfere with vitamin intake. Iron deficiency anemia, vitamin D deficiency, and vitamin B12 insufficiency are common nutritional shortages. Symptoms of dietary deficiencies vary based on the vitamin in question, but they might include weariness, skin diseases, weakness, and muscular pains, among other things. Treatment for nutritional deficiencies often entails increasing the deficient nutrient’s food intake and, in severe situations, supplementing with oral or intravenous forms of the missing vitamin.
Skin traumatism
Skin trauma is defined as physical injury to the skin produced by many reasons, such as bruises, cuts, burns, puncture wounds, and abrasions. Skin damage can range in intensity from minor to severe, with symptoms such as pain, swelling, redness, bleeding, and bruises. Treatment for skin damage varies according to the kind and degree of the injury, but may involve wound care, pain management, and antibiotics if the infection is a concern. Scars can form due to skin injuries in some situations, and extra treatment, such as surgery or skin grafting, may be required to decrease their appearance.
Stress and poor hygiene are lifestyle issues
Stress and bad hygiene are examples of lifestyle problems that can have a negative effect on a person’s health and well-being.
Stress is a normal reaction to difficult or demanding circumstances, but when it becomes persistent or overwhelming, it can lead to a variety of health issues such as anxiety, melancholy, high blood pressure, heart disease, and digestive disorders. Stress can be reduced by implementing healthy living practices such as regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and calming methods such as meditation or deep breathing.
Poor sanitation, such as not cleaning hands, brushing teeth, or bathing on a regular basis, can contribute to the spread of infectious illnesses and contribute to skin and other health issues. Observing excellent sanitation habits, such as hand washing.
The symptoms of skin and its diagnosis
- Rashes or skin redness
- Itching or burning feelings
- Bumpy, blistered, or painful skin
- Skin scaliness or peeling
- Skin color or texture changes
- Excessive crusting or discharge from afflicted regions
- Tenderness or discomfort
- Swelling
- Wounds or lesions that are open
Skin illnesses can also create systemic symptoms such as fever, tiredness, or joint discomfort. You should seek medical assistance if you have any worries about your symptoms or skin changes.
Treatment for skin diseases
Many skin problems can be treated. Skin problems are commonly treated using the following methods:
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are medications that prevent histamine, a chemical generated by the body during an allergic response, from acting. They frequently treat allergy symptoms such as runny nose, watery eyes, itching, hives, and sneezing. Antihistamines are available without a prescription and over the counter and can be administered orally or topically. Drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness are some of the most prevalent adverse effects of antihistamines.
Creams & ointments with medicinal properties
Many creams and ointments with medicinal qualities are available to address a variety of skin diseases and illnesses. Here are a couple of examples:
Antibacterial lotions and ointments are used to prevent and cure bacterial skin diseases such as impetigo and cellulitis. They comprise neomycin, bacitracin, or mupirocin as active components.
Acne lotions and ointments are used to cure acne and to minimise the look of pimples and blemishes. They include chemicals like benzoyl peroxide, glycolic acid, and retinoids.
Burn creams and ointments are applied to small wounds to avoid infection. Silver sulfadiazine and bacitracin are among the components.
Corticosteroid lotions and ointments are used to relieve the itching and inflammation caused by skin diseases such as dermatitis, psoriasis, or allergic responses. They comprise hydrocortisone, betamethasone, or clobetasol as active components.
Antifungal lotions and ointments: These are used to treat fungal diseases of the epidermis, such as ringworm, athlete’s foot, or jock itch. Miconazole, clotrimazole, and terbinafine are among the components.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are medications that treat bacterial illnesses. They function by either killing or stopping bacteria from replicating. Antibiotics are ineffective against viral illnesses like the common cold or flu. Penicillin, amoxicillin, and erythromycin are examples of common antibiotics. To guarantee that all bacteria are destroyed and to avoid the development of antibiotic resistance, it is critical to take antibiotics exactly as recommended and not to stop taking them early, even if you feel better. Antibiotic overuse can potentially lead to antibiotic resistance, making it more difficult to treat illnesses in the future.
Injections of vitamins or steroids
Vitamin or steroid injections are used to address a range of medical conditions. Here are a couple of examples:
Vitamin B12 injections are used to address a vitamin B12 shortage, which can cause exhaustion, weakness, and anaemia. The injection skips the digestive system, allowing for more effective nutrient uptake.
Steroid shots are used to treat inflammation and edoema caused by diseases such as arthritis, bursitis, or tendinitis. They are also useful in the treatment of allergic responses and autoimmune diseases. Cortisone, hydrocortisone, and triamcinolone are common steroids used in shots.
Vitamin D injections: Vitamin D injections are used to address vitamin D deficiency, which can cause brittle bones, muscular fatigue, and other health issues. The injection enables for more effective vitamin uptake.
Vitamin K injections are used to address bleeding conditions or to avoid bleeding in infants at risk of vitamin K deficiency.
Vitamin C injections are sometimes used as an alternative treatment for diseases such as cancer, fatigue, or persistent discomfort. However, there is little empirical proof to back up the efficacy of these injections.
Laser treatment
Laser skin treatment is a cosmetic technique that employs concentrated light radiation to enhance the look of the skin. Laser treatments are used to treat various skin issues, including
- Fractional laser resurfacing, a treatment method for wrinkles, fine lines, acne scars, and sun damage.
- IPL treatment (intense pulsed light) cures age spots, UV damage, and broken capillaries.
- YAG laser is used to cure birthmarks, dark spots, and tattoos.
- The CO2 laser is used to cure deep wrinkles and skin tightening.
Side effects of laser treatments include redness, swelling, and soreness, although these normally go away within a few days. Selecting a trained and experienced laser therapy practitioner and communicating any concerns is critical.
Certain prescribed drugs
Certain prescription medications are used to address a wide range of medical problems. Here are a couple of examples:
- Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial illnesses like strep throat, urinary tract infections, and asthma.
- Antidepressants are medications that are used to address melancholy, anxiety disorders, and other mental health issues.
- Antihistamines are medications that are used to treat allergy responses like hay fever, rashes, and allergic conjunctivitis.
- Opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) are used to manage pain caused by accidents, surgeries, or chronic diseases like arthritis.
- Statins are medications that are used to decrease cholesterol levels and lower the chance of heart disease.
- ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers are used to manage high blood pressure and lower the chance of stroke, heart attack, and other complications.
- Chemotherapy medicines are used to cure cancer by either killing or slowing the development of cancer cells.
- Insulin is used to manage diabetes by controlling blood sugar levels.
Flare-ups of the skin
Not all skin illnesses respond to therapy, and some conditions resolve on their own.
People with chronic skin conditions frequently experience severe symptoms. People can sometimes force incurable diseases into remission. However, most skin diseases resurface due to particular triggers, such as stress or sickness.
Temporary and cosmetic skin siseases are frequently treated with:
- Makeup that is medicated
- OTC (over-the-counter) skin care products
- Good hygiene habits
- Modest lifestyle changes, such as food modifications
Skin disorders that are not contagious
Acne and atopic dermatitis are two examples of noninfectious skin problems that can be avoided. Prevention methods differ depending on the condition. Here are some prevention tips for noninfectious skin disorders:
- Every day, wash your face with a light cleanser and water.
- Apply moisturiser.
- Avoid allergies in the surroundings and in your diet.
- Avoid coming into touch with corrosive chemicals or other irritants.
- Sleep for at least 7 hours each night, as sleep deprivation can worsen many skin conditions.
- Consume a well-balanced diet.
- Keep your skin safe from extreme cold, heat, and wind.
Prevention of skin diseases
Certain skin diseases, such as genetic conditions and skin problems caused by other illnesses, are unpreventable. Some skin problems, however, can be avoided.
To avoid contagious skin problems, follow these guidelines:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and warm water.
- Avoid sharing utensils and drinking glasses with others.
- Avoid coming into direct contact with the infected skin of others.
- Before utilizing objects in public places, such as gym equipment, clean them.
- Personal goods such as blankets, hairbrushes, and swimwear should not be shared.
- Each night, get at least 7 hours of sleep.
- Consume lots of water.
- Excessive physical or emotional stress should be avoided.
- Consume a well-balanced diet.
- Get immunized against contagious skin disorders like chickenpox.
Conclusion
The skin is affected by a variety of conditions. Some are long-term, while others are very brief. Some conditions are painful or unpleasant, but they are not dangerous. Other disorders, such as skin cancer, can be fatal.
The underlying cause determines the therapy for each. It’s a good idea to consult a doctor if you notice any new or odd skin issues.












